
Daily Threat Intel by CyberDudeBivash
Zero-days, exploit breakdowns, IOCs, detection rules & mitigation playbooks.
Follow on LinkedIn Apps & Security Tools
Explore CYBERDUDEBIVASH ECOSYSTEM , Apps , Services , products , Professional Training , Blogs & more Cybersecurity Services . https://cyberdudebivash.github.io/cyberdudebivash-top-10-tools/ https://cyberdudebivash.github.io/CYBERDUDEBIVASH-PRODUCTION-APPS-SUITE/ https://cyberdudebivash.github.io/CYBERDUDEBIVASH-ECOSYSTEM https://cyberdudebivash.github.io/CYBERDUDEBIVASH © 2026 CyberDudeBivash Pvt. Ltd. | Global Cybersecurity Authority Visit https://www.cyberdudebivash.com for tools, reports & services Explore our blogs https://cyberbivash.blogspot.com https://cyberdudebivash-news.blogspot.com & https://cryptobivash.code.blog to know more in Cybersecurity , AI & other Tech Stuffs.
Executive Summary
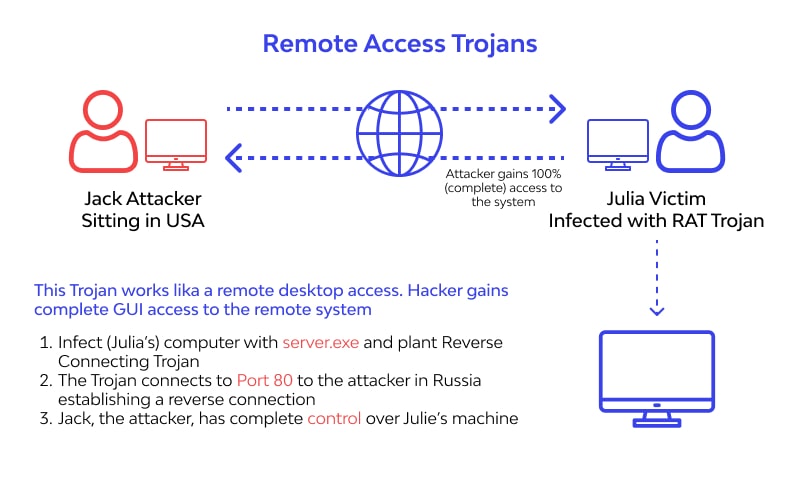
ModeloRAT is a newly identified, previously undocumented Remote Access Trojan (RAT) observed in active campaigns targeting Windows environments. The malware demonstrates modular design, stealth-focused persistence, and dynamic command-and-control (C2) behavior, indicating a professionally developed threat likely intended for long-term espionage, credential theft, and post-exploitation operations.
Initial analysis suggests ModeloRAT is positioned between commodity RATs and advanced persistent tooling, blending common RAT capabilities with evasion-aware engineering choices.
Malware Classification
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Malware Type | Remote Access Trojan (RAT) |
| Platform | Microsoft Windows |
| Architecture | x86 / x64 |
| Execution Context | User-level (Privilege Escalation optional) |
| Persistence | Registry + Scheduled Tasks |
| C2 | HTTP(S) with dynamic endpoints |
| Obfuscation | String encryption, API hashing |
| Status | Undocumented / Emerging Threat |
Infection Vector & Initial Access
Observed infection chains indicate multiple delivery mechanisms, increasing campaign flexibility.
Common Vectors
- Malicious email attachments (ZIP / ISO / LNK)
- Trojanized cracked software installers
- Drive-by downloads via compromised websites
- Loader-based delivery (dropper → payload)
Execution Flow
- User executes initial loader
- Loader decrypts ModeloRAT payload in memory
- Payload injected into a trusted Windows process
- Persistence established
- C2 beacon initiated
Core Capabilities



4
Credential Harvesting
- Browser credential extraction
- Clipboard monitoring
- Keylogging via low-level keyboard hooks
- Potential LSASS interaction (post-priv escalation)
Remote Control
- Execute shell commands
- Upload / download arbitrary files
- Remote desktop screen capture
- Webcam & microphone surveillance (optional module)
Data Exfiltration
- Encrypted HTTP POST requests
- Chunked data transfer to evade size-based detection
- Adaptive beacon intervals
Modular Architecture
ModeloRAT follows a plugin-based architecture, allowing operators to deploy only required functionality.
Known / Suspected Modules
core.dll– main RAT logicgrabber.dll– credentials & browser dataspy.dll– keylogging, screen capturenet.dll– C2 communicationpersist.dll– autorun & task scheduling
Modules are loaded on-demand, reducing behavioral footprint during idle phases.
Persistence Mechanisms
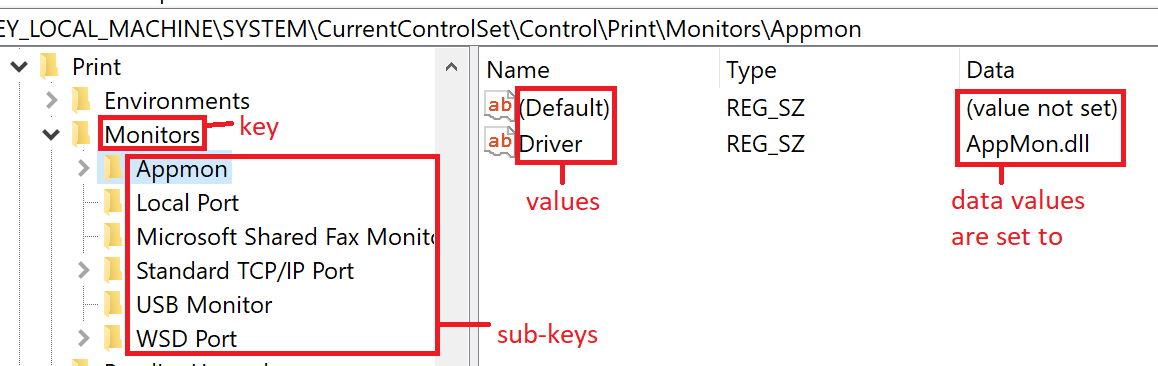

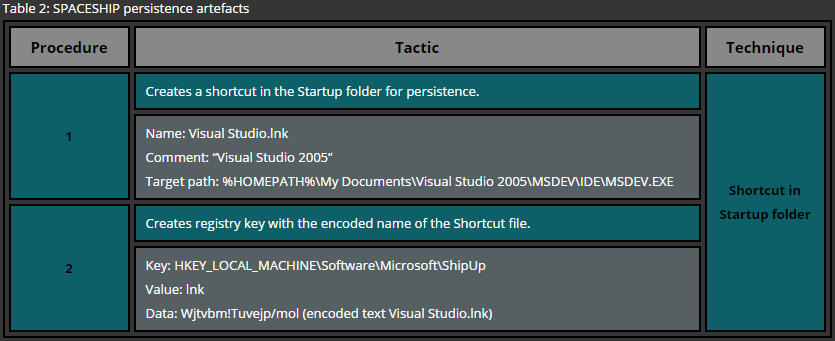
Techniques Observed
- Registry Run keys
HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run - Scheduled Task masquerading as system updater
- Optional startup folder drop (fallback)
Persistence names mimic:
- Windows Update
- Device Manager
- Graphics Driver services
Command-and-Control (C2)
C2 Characteristics
- Hardcoded seed domains
- Runtime-resolved endpoints
- TLS-encrypted traffic
- Custom User-Agent strings
- Periodic heartbeat beacons
Anti-Takedown Strategy
- Domain rotation
- IP fallback lists
- Sleep-jitter to evade sandbox timing
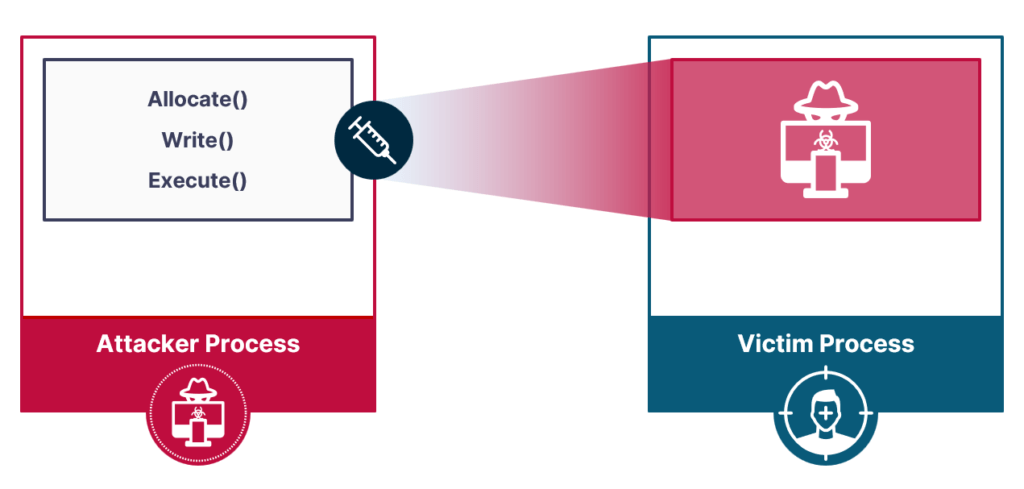
Evasion & Anti-Analysis
ModeloRAT incorporates defensive awareness, although not at nation-state level.
Techniques
- API hashing (GetProcAddress avoidance)
- Encrypted strings (runtime decryption)
- Sandbox detection (sleep timing, CPU count)
- Debugger checks
- Process injection into trusted binaries
Indicators of Compromise (Generic)
File System
%AppData%\Microsoft\<random>.exe%Temp%\mdl_<random>.bin
Registry
- Suspicious Run key entries
- Randomized task names with system-like descriptions
Network
- Repeated outbound HTTPS POSTs
- Small encrypted payloads at fixed intervals
Final IOCs should be environment-specific and campaign-correlated.
Threat Assessment
| Factor | Risk |
|---|---|
| Stealth | High |
| Impact | High |
| Detection Difficulty | Medium–High |
| Target Scope | Consumer + Enterprise |
| Campaign Maturity | Growing |
ModeloRAT is not noisy, making it suitable for long-term access rather than smash-and-grab attacks.
Defensive Recommendations
Immediate Actions
- Enable EDR behavioral rules for:
- Process injection
- Suspicious scheduled tasks
- Monitor registry autorun locations
- Enforce least-privilege user policies
Strategic
- Network TLS inspection (where legal)
- Threat hunting for anomalous beacon patterns
- Email attachment sandboxing
- Disable macros and LNK execution where possible
Analyst Conclusion (CyberDudeBivash)
ModeloRAT represents a new generation of quietly capable RATs — not groundbreaking individually, but dangerous in aggregate. Its modular design, persistence reliability, and evasive execution suggest active development and potential future evolution into a broader malware framework.
Organizations should treat ModeloRAT as an early-warning signal, not a one-off curiosity.
#ModeloRAT #MalwareAnalysis #RemoteAccessTrojan #ThreatIntelligence
#WindowsMalware #CyberSecurityResearch #ReverseEngineering
#IncidentResponse #EDR #CyberDudeBivash
Leave a comment